Welcome
This eCourse is designed to help you integrate the information in the post “Is Smoking Vegan?“
Learn about the various issues affecting the “vegan-ness” of smoking, including: the hidden ingredients in cigarettes, animal testing in the tobacco industry, worker conditions on plantations, the environmental impact of smoking, and more!
Course Video & Article
Despite decades of debate, denial, and dubious behavior on the part of the tobacco industry regarding the potential dangers of cigarettes, it’s now generally agreed upon that smoking is bad for your health. Smoking damages nearly every organ in the body, causing strokes, coronary heart disease, respiratory diseases, a whole slew of cancers, and other deleterious effects.1 And while big tobacco has done its best to feign ignorance since the 40’s, we now know the answer to “Is smoking bad for you?” is a resounding yes. But a less-hotly debated question remains: is smoking vegan?
While being vegan is often associated with a level of health fanaticism approaching daily wheatgrass juice enemas and coffee colonics, the truth is, not everyone goes vegan for their health. There are junk food vegans, vegans who drink alcohol, and yes—even vegans who smoke.
But, can cigarettes be considered vegan? As usual, the answer to this question is more complex than it would first appear. I’m going to touch on the various areas of concern, but please refer to this article’s citations for more detailed information.
Animal Ingredients: Pig’s blood, Beeswax and Beaver Anal Sacs
The most basic measure of whether something is vegan or not is whether it contains animals or their byproducts. When we combine the myriad of ways we disguise animal byproducts with the close to 600 ingredients found in cigarettes,2 including arsenic, formaldehyde, lead, ammonia, acetone and other far less-pronounceable elements, it becomes rather difficult to ascertain if anything is animal-derived.
This issue was brought to a very public head back in 2010 when a press release, light on the facts but big on the sensation, claimed that cigarettes may contain pig’s blood.3 [tweet this] This revelation came from an artist Christien Meindertsma’s three-year-long project Pig 05049, which tracked and documented all of the ways one pig’s body was used post-slaughter, including in cigarette filters.4
Anti-smoking advocate Professor Simon Chapman of the University of Sydney saw this as an opportunity to use public outrage, particularly among Jewish, Muslim, vegetarian and vegan populations, to bring to light “concerns that ingredients such as additives or processing aids used in tobacco products are virtually unregulated and non-transparent.”5
After creating the press release, the story went viral and built into quite a frenzy, with Iranian officials calling it a Zionist conspiracy6 and tobacco companies churning out denials left and right. The truth of the matter is far less titillating. In 1997 a Greek tobacco company set out to create a healthier cigarette, using pig’s blood in the filter to mitigate toxins. The resulting BioFilter led the company to second place in the Greek tobacco industry, though every scientific study to evaluate these claims found them to be patently false,7 and in 2002 Greece finally outlawed their “healthier smoking” claims. As far as I can tell, the filters are still on the market and I have link below to the company’s website with more information.8
There are also at least two other animal-derived ingredients in cigarettes, which are far more regularly employed: beeswax and castoreum. Beeswax is rather self-explanatory and you can see my videos here on the vegan-ness of bee products for more information. Castoreum, used in cigarettes to lend a sweet, smoky flavor, is another matter entirely.
Castoreum, the source of artificial raspberry, vanilla and strawberry flavors, is an extract made from the dried, ground up anal sacs located by the anal glands of beavers. Castoreum be added to foods such as gums, alcohol, candy and baked goods. Castoreum is harvested by killing beavers and cutting out their castor glands,9 making it a most definitively un-vegan ingredient.
So when it comes to animals in your smokes, bees and beaver butts are more likely than pigs blood, but just as un-vegan. [tweet this]
The Animal Toll of Tobacco Farming
Now I’ll just speak very briefly to the concern of animals killed during tobacco farming and harvesting. While we should strive for pesticide-free, sustainable farming, with any crop, field animals are going to be unintentionally harmed and killed in the farming and harvesting process. We have to eat but we don’t have to smoke, so the animals killed by tobacco farming are entirely avoidable deaths.
Animal Testing and the Tobacco Industry
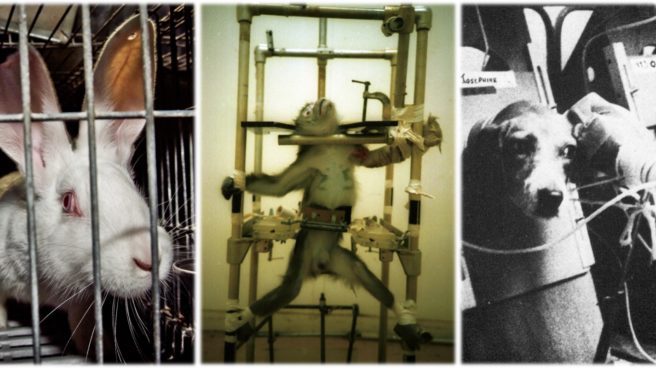
And now, to the heavy-hitter of the vegan cigarette debate: animal testing.[tweet this] I have a four-part video series on animal testing which goes into greater detail about the inefficacy of animal tests, why we are still conducting them, how they endanger and even kill humans, and what viable alternatives exist, which I’ve linked up here and below if you want to delve deeper into this matter.
Perhaps the most insane aspect of animal testing as a whole is its complete and utter lack of credible results. It’s no secret that our bodies differ greatly from other species, and so, it follows, would our reactions to stimuli and toxins.
In regards to tobacco specifically, Dr. C Ray Greek of Americans for Medical Advancement states that “Animal experiments failed notoriously to demonstrate a smoking-cancer connection for over half a century…If the greatest killer of our time was promoted by physicians based on animal experiments, there is obviously something terminally wrong with the system.”10
A 2015 paper drawing on more than 50 recent toxicology studies, demonstrated the superiority of widely available modern, non-animal models over inaccurate animal tests for measuring the toxicity of tobacco products.11 In 2012, the U.S. Congress even stated that “there is significant scientific evidence that animals are poor models for the testing of tobacco products used by humans.”12
Unlike all medications, tobacco products are not required to undergo animal testing. The UK, Germany, Belgium and other countries even banned their usage and Canada requires only in vitro studies, meaning on a cellular level rather than on whole living animals.13
Even the tobacco industry’s own studies have concluded that “in vitro toxicology tests can be successfully used both for better understanding the biological activity of cigarette smoke… and for guiding the development of cigarettes with reduced toxicity.”14 Despite this fact, tobacco companies, government agencies,15 the American Cancer Society, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, among other organization and, yes, even anti-smoking groups continue to test cigarettes on animals.
The citations and bibliography at the base of this post contain several articles and studies that catalog, describe, and demonstrate the myriad of horrifying animal tobacco tests—we’ll16 only cover a few explicitly in this article.
Direct Smoking Tests
Perhaps the most visually shocking type of tobacco testing are the direct smoking tests, made famous in 1975 by undercover Sunday People reporter Mary Beith in her expose known as “The Smoking Beagles.” Beith got a position in an Imperial Chemical Industries laboratory where 48 beagles were restrained with straightjackets, placed into what Beith described as “medieval stocks” and fitted with tubed masks which forcibly pumped cigarette smoke into their lungs day in and day out for up to three years for some of the dogs. Beith reported that, “when they have finished their smoking stint the dogs are killed and sent to pathology laboratories to be cut up and examined for signs of cancer, liver or heart diseases or other possible effects. Some of the dogs have acquired a smoker’s cough judging from the sounds I heard.”17
The images Beith captured sparked global outrage, yet only two of the 48 beagles were rescued in a technically illegal act of liberation by activist Mike Huskisson and an unnamed partner in the early days of the Animal Liberation Front.18
While not garnering the same level of disgust from the public, direct smoking tests on mice and rats are just as horrifying. Their entire bodies are crammed into tiny canisters that pump smoke directly into their noses for six or more hours a day up to two years.19
Direct smoking tests can also involve tracheotomies. In a 2001 study at the Oregon National Primate Research Center involving sixty-seven pregnant Rhesus macaque monkeys, half of the monkeys had tubes surgically implanted in order to subject them to a continuous flow of nicotine for the last four months of their pregnancies. Five days before the mothers reached full term, the experimenters cut out, killed and dissected the fetuses of all 67 mothers.20
These kind of experiments are still being carried out on mice, rats, beagles, monkeys, apes, and other sentient beings. [see all studies below] They are not required by law, have no scientific validity and they even endanger humans with the cross-species application of their results, and are all for a product that is not only completely unnecessary but also deadly to consumers and damaging to the environment.
The Environmental Impact of Smoking
Speaking to the environmental impact of smoking, around 5.6 trillion cigarette butts are dumped into the environment every year. When these butts land in water or on the soil, all of the chemicals and carcinogenic ingredients we discussed creates leachates, a toxic soup that poisons fish and other wildlife.21
The Harm to Companion Animals: Second-Hand Smoke
Of course smoking also affects one’s home environment as well. A series of studies at Tufts University and Colorado State University found that second hand smoke is just as harmful to companion animals as it is humans. Cats living with smokers are twice as likely to develop malignant lymphoma, and dogs living with smokers develop cancers of the nose and sinus area, all of which are terminal within a year.22
The Human Cost of Tobacco: Child Labor and Worker Toxicity Exposure
And then there’s the human cost of tobacco farming. Green Tobacco Sickness (GTS) is caused by the constant exposure of workers to the nicotine of the plants, which is absorbed through their skin.23 This is exacerbated in the case of child workers and child labor is a major issue within America’s tobacco farming. While several countries, including major tobacco producers such as Brazil and India, prohibit children under 18 from working on tobacco farms, in the US children as young as 12 work in fields for 50 to 60 hours a week in extreme heat and with ongoing exposure to pesticides and nicotine.24
The Health Consequences of Smoking
And of course, there are the health consequences, which may or may not even be an inherently vegan issue, and which is thoroughly documented elsewhere. If you are a smoker and want to stop for any reason, please see the list of resources to quit smoking below for support.
In Closing…
I hope that this video has been helpful. I’d love to hear your thoughts- do you think smoking can be considered vegan? If you were a smoker who went vegan, did you quit? Are you a vegan smoker now? Are you a non-vegan smoker wanting to go vegan but overwhelmed that now you have to ditch the cigarettes too? [If so, personally, I’d say focus on the meat, dairy, eggs and honey first and then tackle big tobacco.]
The time it to produce this video clocks in at around 52 hours. If you’d like to help support Bite Size Vegan so I can keep putting hours to bring you this educational resources, please check out the support page where you can give a one-time donation or receive perks and rewards for your support by joining the Nugget Army.
If you enjoyed this video, please share it around to help inform others!
— Emily Moran Barwick
Open the accordion above to view the course video and article. Then take the quiz to test your knowledge of the information covered! You may take the quiz an unlimited amount of times. Passing score: 80%
NOTE: I’ve recently re-worked the eCourses so that you no longer have to register to take the quiz! As this is a big change, if you find any technical issues with taking the quiz, please do let me know by reporting it here (opens in new tab). Thank you!
"*" indicates required fields